Traps for catching garden pests can be viewed here.
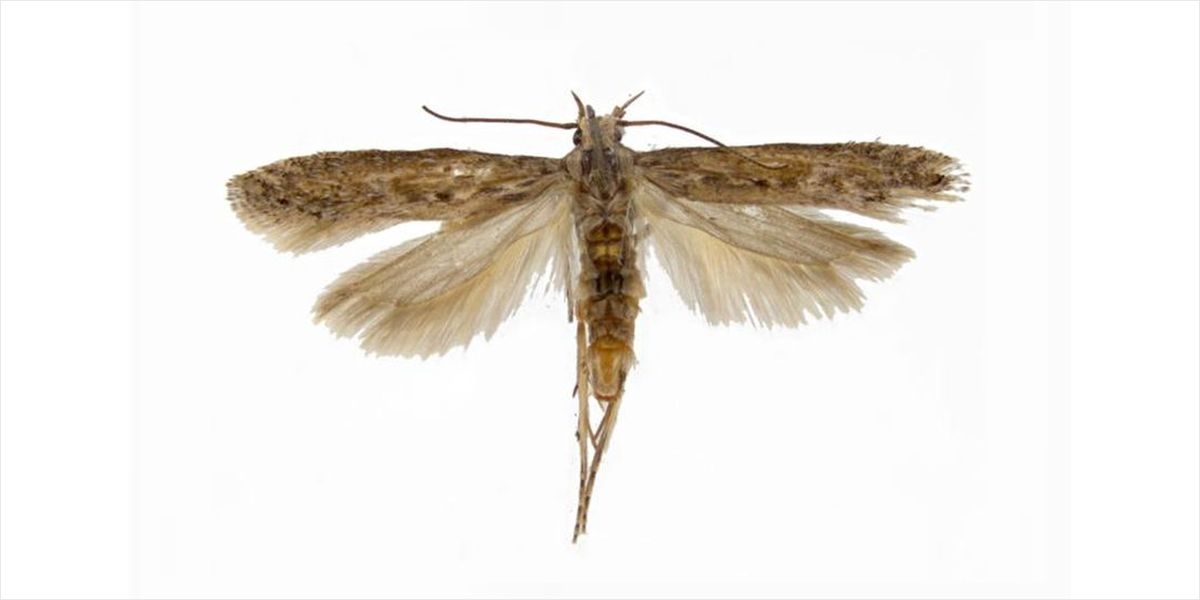

Potato tuber moth - is a pest of plants of the nightshade family (potatoes, eggplants, tobacco, tomatoes, peppers, physalis). Caterpillars are harmful. Reproduction is bisexual. Development is complete. During the year, the development of from 2 to 14 generations can be observed, depending on the climate of the location. Caterpillars that have completed their development and cocoons overwinter. Object of external and internal quarantine.
Morphology
Imago
A butterfly with a wingspan of 12-16 mm. The forewings are broadly lanceolate, brown-gray in color, dark along the inner edge. Yellow scales and dark brown streaks are scattered over the entire surface of the front wings. The hind wings have a notch along the outer edge and a fringe, the length of which exceeds the width of the wing.
When at rest, the wings are folded on the back. The antennae are bristle-shaped, multi-segmented, composed of well-defined black segments, lighter on the underside. The labial palps extend behind the head and reach the posterior edge of the eye.
The legs increase in size from the front to the back pair. On the middle pair at the top of the tibia there is one pair of spurs. There are two pairs of spurs on the hind legs. One pair is located at the top of the shin, and the second is in the middle. The internal spurs are much longer than the external ones.

Sexual dimorphism
Individuals of different sexes differ in the structure of their genital organs.
Male. On the anterior edge of the hind wing there is a brush of long hairs (frenulum), reaching the middle of the wing. The wingspan is 2 - 2.5 mm shorter than that of the female.
Female. The wingspan is larger than that of the male and is 12 - 15 mm.
Egg
The egg is oval. Freshly laid aside, it is pearly white. Length - up to 0.8 mm. Width - 0.45 - 0.55 mm. As the embryo develops, the egg darkens. Before exiting, the caterpillar is viewed through the shell.
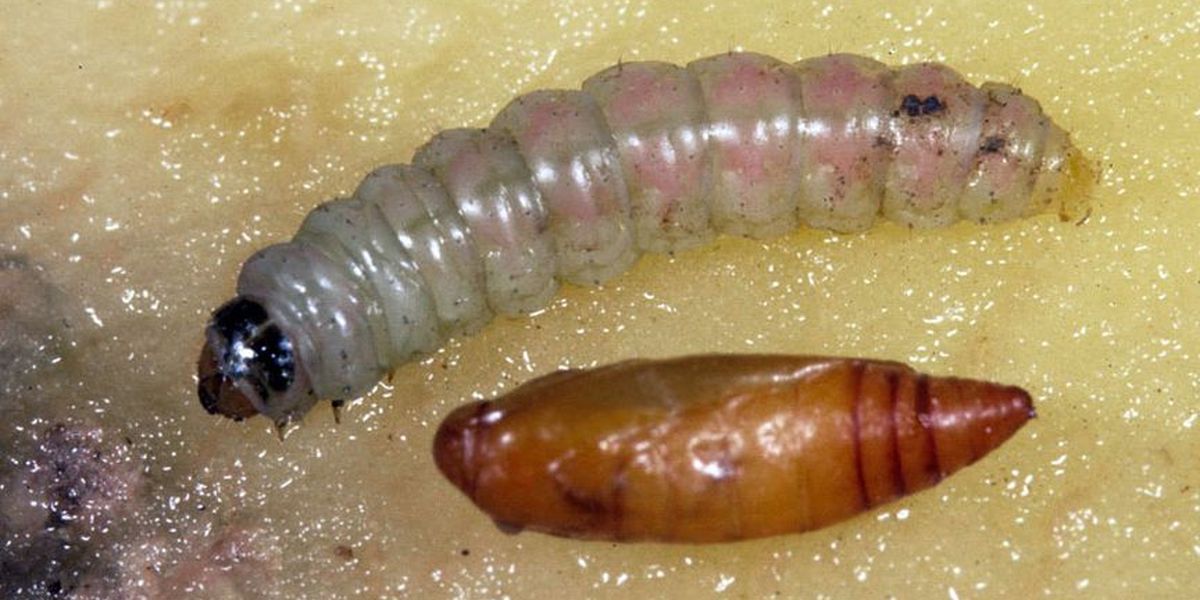
Larva
The larva (caterpillar) is yellowish-pink or gray-green, with a longitudinal stripe in the middle of the back and small scutes along the body. The chest shield is black, the anal shield is yellow. The length of the caterpillar is 8-10 mm. or 10 - 13 mm.
Pupa
The pupa is brown, with a small cremaster and setae at the end of the abdomen. Develops in a silky silver-gray cocoon. The length of the pupa is 5-6.5 mm. Cocoon length - 1 cm. Width - 1-2 mm. The male pupa cocoon is smaller than the female pupa cocoon.
Development
Imago
The flight of butterflies of the first generation of potato moth begins at the end of April - in May with activity both at night and during the day. In areas with a hot climate (southern Ukraine), butterfly activity is observed at night from sunset to sunrise and 1-2 hours after sunrise. Adults can tolerate temperatures down to -1°C for two weeks. In winter, at a temperature of 10°C, single individuals can be observed. In the autumn period of years it is observed in the daytime and is especially intense at a temperature of 18°C. Flight activity is observed at a temperature of 14°C. The lifespan of adults is 10 - 12 days.
Adults emerge from the pupae, mate and lay eggs.
Mating period
A day after mating, the females lay 2-3 eggs, placing them on the bottom of the leaves, on the stems, soil, and bare potato tubers. Laying takes place within 2-16 days. During this time, one female is capable of laying up to 300 eggs. On average, the fertility of potato moth is 150-200 eggs.
Egg
Embryonic development lasts from 3 to 15 days, depending on temperature conditions. The lower threshold for egg development is + 9.5°C. At temperatures above the threshold, development is not interrupted.
Larva
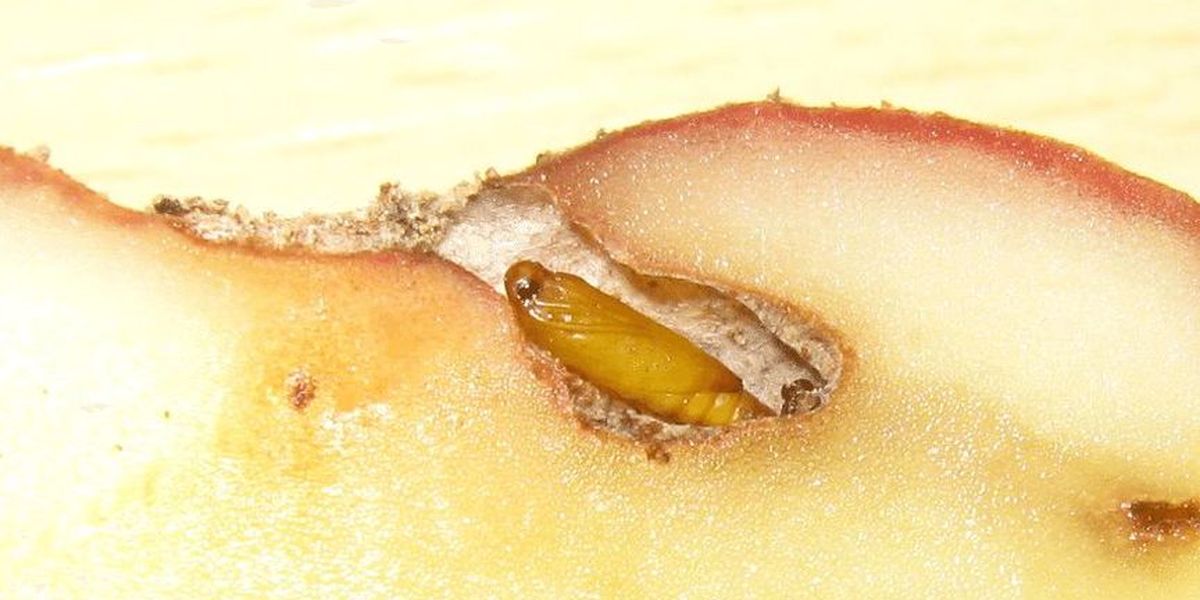
The larva (caterpillar) immediately after rebirth bites into the epidermis of a leaf, young shoot or tuber peel. The transition of caterpillars into potato tubers is observed as the leaves and stems age. In tubers, caterpillars make passages under the skin, which leads to its drying out, precipitation and scarring. They can penetrate deep inside the tubers, gnawing through winding passages 2-3 mm in diameter, filling them with excrement. This leads to rotting of the tubers. Purple color appears in places where the pest has penetrated. Caterpillars are able to move from potatoes to other plants of the nightshade family, including garbage. They can damage the fruits of tomatoes, eggplants and other nightshades by gnawing holes inside and filling them with excrement. The surface of the fruit becomes scarred and deformed. One fruit can feed several caterpillars at the same time.
After 11-14 days, under optimal development conditions at a temperature of +22 +27°C, the caterpillars leave the mines, weave cocoons in the upper layers of the soil between dry leaves, in soil cracks, in plant debris, between tubers in vegetable stores and other secluded places, where they pupate. Older caterpillars and pupae overwinter.
Pupa
The pupa develops for 7-12 days in a cocoon of a grayish-silver color, different from the cocoons of other moths. The caterpillars first make a silky mesh, then form an outer layer, to the surface of which lumps of earth and debris are attached. When developing in storage facilities and drying rooms, the caterpillars pupate in cracks in walls, folds of bags, and among debris on the floor.

Abiotic factors
In warm summer weather, the development of one generation lasts 3-4 weeks. A large number of generations are formed (from 2 to 14), which leads to overlap in time.
At a temperature of +20+ 27°C, one generation of moths develops within 28 - 30 days. At a temperature in vegetable stores of +15 + 20°C, the development of one generation lasts 60 - 70 days, and when the temperature fluctuates from + 8°C to + 20°C, about 120 - 150 days. At a temperature of 10°C, moth development lasts up to 200 days, and at + 35°C - 16 days. At -4°C and +36°C all stages of development die. Therefore, during the growing season, all stages of the pest are observed simultaneously. In Ukraine, butterfly years occur almost continuously from April to November. The species does not have diapause and does not tolerate cold winters, but is well preserved and develops in vegetable stores at temperatures above +4°C. In the spring, when planting potatoes, moths again enter the fields.
It has been established that in temperature-controlled storage facilities at an optimal temperature within + 3 + 5°C, all stages of the pest die within four to five months.
Potato tuber moth - is an object of external and internal quarantine. Caterpillars are harmful. Potatoes, tobacco, eggplant, tomato, datura, nightshade and other crops and weeds from the nightshade family are damaged. Moths cause especially severe damage to vegetables from the nightshade family during storage.



